Function and Immunogenicity of Regenerative Cellular Therapies
Function and Immunogenicity of Regenerative Cellular Therapies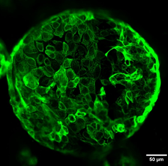
A key focus of the Saeb-Parsy Lab is collaborative examination of the in vivo function and immunogenicity of human stem cells and regenerative cellular therapies using a range of immunodeficient and humanised mouse models. Through long-standing collaborations with Prof Ludovic Vallier and Dr Cedric Ghevaert from the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute and Dr Meritxell Huch from the Gurdon Institute, we are examining the function and immune response to cellular therapies derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and organoids for the treatment of diabetes, cholangiopathies and platelet deficiencies.
In collaboration with Dr Athina Markaki from the Department of Engineering, we are also working on using these cellular therapies to create complex bioengineered tissues, including neo-bile ducts, for transplantation. Successful cryopreservation of such complex cellular aggregates is a key hurdle to the clinical translation of bioengineered tissues. To address this outstanding challenge, we are collaborating with Prof Nigel Slater from the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology to investigate novel methods for the cryopreservation of cellular aggregates, including pancreatic islets with Mr John Casey from the Scottish Islet Laboratory.
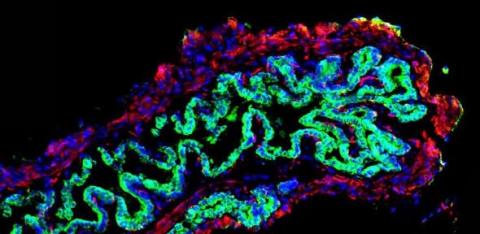 Much of our research program in regenerative medicine is underpinned by the use of human haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), including in collaboration with Dr Elisa Laurenti from the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute. A particular focus of our group is using human HSCs for the creation and characterization of experimental models of the human immune compartment, also known as ‘humanised mice’. Our fundamental approach is to use tissue donated by deceased human organ donors to reconstitute the immune compartment of immunodeficient mice and to generate cellular therapies of interest, while using the same primary cells and tissues as appropriate controls. I am the co-founder and coordinator of the annual UK Humanized Mouse Symposium, which aims to share expertise and encourage collaborations focused on the characterization and use of this important experimental model.
Much of our research program in regenerative medicine is underpinned by the use of human haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), including in collaboration with Dr Elisa Laurenti from the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute. A particular focus of our group is using human HSCs for the creation and characterization of experimental models of the human immune compartment, also known as ‘humanised mice’. Our fundamental approach is to use tissue donated by deceased human organ donors to reconstitute the immune compartment of immunodeficient mice and to generate cellular therapies of interest, while using the same primary cells and tissues as appropriate controls. I am the co-founder and coordinator of the annual UK Humanized Mouse Symposium, which aims to share expertise and encourage collaborations focused on the characterization and use of this important experimental model. 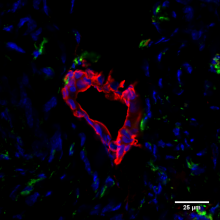
Kourosh is the Principal Investigator for the BETA-Protect collaboration which brings together investigators from Cambridge, London, Edinburgh, and Edinburgh to investigate the immunogenicity of regenerative cellular therapies for the treatment of type I diabetes and to optimize personalized immunotherapies to prevent their rejection. He is also a co-investigator in the LSFM4Life European Consortium which aims to develop and optimize organoids derived from adult pancreas tissue for treatment of type 1 diabetes.
To support collaborative research using human tissue and expedite efficient in vivo translation of world-class laboratory research, the Saeb-Parsy lab has founded and directs the Cambridge Biorepository for Translational Medicine and the Cambridge In Vivo Assessment Platform.
Selected Related Publications
- Sampaziotis F, Justin AW, Tysoe OC, Sawiak S, Godfrey EM, Upponi SS, Gieseck RL, de Brito MC, Berntsen NL, Gómez-Vázquez MJ, Ortmann D, Yiangou L, Ross A, Bargehr J, Bertero A, Zonneveld MCF, Pedersen MT, Pawlowski M, Valestrand L, Madrigal P, Georgakopoulos N, Pirmadjid N, Skeldon GM, Casey J, Shu W, Materek PM, Snijders KE, Brown SE, Rimland CA, Simonic I, Davies SE, Jensen KB, Zilbauer M, Gelson WTH, Alexander A, Sinha S, Hannan NRF, Wynn TA, Karlsen TH, MelumE, Markaki4 AE, Saeb-Parsy K*, Vallier L* (2017). Reconstruction of the murine extrahepatic biliary tree using primary human extrahepatic cholangiocyte organoids. Nature Medicine (2017) In press (* equal contribution)
- Kilbride P, Mahbubani KT, Saeb-Parsy K, Morris GJ (2017) Engaging Cold to Upregulate Cell Proliferation in Alginate-Encapsulated Liver Spheroids. Tissue Engineering Part C Methods (in press).
- Sampaziotis F, Brito MC, Bertero A, Madrigal P, Saeb-Parsy K, Soares F, Schrumpf E, Melum E, Karlsen TH, Bradley JA, Gelson WTH, Davies S, Baker A, Kaser A, Alexander GJ, Hannan NRF, Vallier L (2015) Cholangiocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells for disease modeling and drug validation. Nature Biotechnology 33: 845-52.
